As Saudi Arabia accelerates its digital transformation under Vision 2030, cybersecurity has become a cornerstone of business continuity for organizations across Saudi Arabia. As the Kingdom advances its Vision 2030 digital transformation initiatives, the need for robust security operations has never been more critical. For business leaders and IT decision-makers, understanding SOC implementation is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Understanding SOC Implementation in the Saudi Context
SOC implementation refers to the strategic establishment of a Security Operations Center—a centralized unit that monitors, detects, analyzes, and responds to cybersecurity incidents in real-time. For Saudi organizations navigating increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, a well-structured SOC implementation serves as the foundation of an in-depth security posture.
The question many business leaders ask is: What does SOC stand for in business? Simply put, SOC stands for Security Operations Center, and it represents your organization’s dedicated defense mechanism against cyber threats. It’s where technology, processes, and skilled professionals converge to protect your digital assets around the clock.
Why SOC Implementation Matters for B2B Organizations in Saudi Arabia
Saudi businesses face unique challenges in the cybersecurity landscape. With the National Cybersecurity Authority (NCA) enforcing stringent compliance requirements and cyber threats targeting critical infrastructure, SOC implementation has become a strategic imperative rather than a technical afterthought.
What is a SOC used for? At its core, a SOC provides:
- Continuous monitoring of your network, systems, and applications
- Rapid incident response to minimize damage and downtime
- Threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging risks
- Compliance management aligned with NCA Essential Cybersecurity Controls and international standards
- Security analytics for informed decision-making
For B2B organizations, this translates to protected customer data, maintained business reputation, and uninterrupted service delivery—all critical factors for maintaining competitive advantage in the Saudi market.
The SOC Implementation Journey: From Awareness to Operations
Phase 1: Understanding What is SOC Implementation
Before embarking on SOC implementation, organizations must first understand what this entails. What is SOC in simple terms? Think of it as your organization’s security command center—a dedicated team and infrastructure working 24/7 to keep your business safe from cyber threats.
SOC implementation encompasses several critical components:
- People: Security analysts, incident responders, and SOC managers
- Processes: Documented workflows, incident response procedures, and escalation protocols
- Technology: SIEM platforms, threat intelligence feeds, and security tools
- Governance: Policies, compliance frameworks, and performance metrics
Understanding these foundational elements is crucial before moving forward with your cybersecurity strategy.
Phase 2: Defining Your SOC Process
What is a SOC process? It’s the systematic approach your organization takes to identify, analyze, and respond to security events. A well-defined SOC workflow typically includes:
- Detection: Identifying potential security incidents through continuous monitoring
- Analysis: Investigating alerts to determine their validity and severity
- Containment: Isolating affected systems to prevent threat spread
- Eradication: Removing the threat from your environment
- Recovery: Restoring normal operations safely
- Post-Incident Review: Learning from incidents to improve defenses
Understanding what are SOC processes helps organizations establish clear expectations and measurable outcomes for their SOC implementation initiative. These processes align with frameworks like ISO 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework, which provide internationally recognized standards for security operations.
Phase 3: Choosing Your SOC Operations Model
What are SOC operations? This refers to the day-to-day activities and service delivery model of your Security Operations Center. Saudi organizations typically consider three SOC implementation approaches:
In-House SOC: Building and managing your own security operations center gives you complete control but requires significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and specialized talent. This model suits large enterprises with substantial resources and specific compliance requirements.
Managed SOC Services: Partnering with specialized providers offers access to enterprise-grade security capabilities without the overhead of building internal infrastructure. This approach provides flexibility, expertise, and cost-effectiveness—ideal for mid-sized organizations looking to accelerate their SOC implementation timeline.
Hybrid SOC: Combining internal capabilities with external expertise provides the best of both worlds, allowing organizations to maintain strategic control while leveraging specialized skills for complex scenarios.
How to Implement a SOC: A Practical Roadmap
How to implement a SOC? This question requires a structured, phased approach tailored to your organization’s maturity, resources, and risk profile.
Step 1: Assessment and Planning
Begin your SOC implementation by conducting an advanced security assessment:
- Evaluate your current security posture and capabilities
- Identify critical assets and potential vulnerabilities
- Define your security objectives and success metrics
- Determine budget, timeline, and resource requirements
- Assess compliance obligations under NCA regulations
This initial assessment phase is critical for successful SOC implementation and should involve stakeholders across IT, business units, and executive leadership.
Step 2: Designing Your SOC Architecture
What is SOC L1, L2, and L3? These levels define the tiered structure of SOC operations:
- L1 (Tier 1): Alert monitoring and initial triage—your first line of defense
- L2 (Tier 2): In-depth investigation and incident analysis—experienced analysts
- L3 (Tier 3): Advanced threat hunting and expert-level response—specialized experts
Your SOC implementation should clearly define roles, responsibilities, and escalation paths across these tiers. This tiered approach, detailed in resources like SANS SOC Survey, ensures efficient resource allocation and effective incident handling.
Step 3: Technology Selection and Integration
Successful SOC implementation requires the right technology stack:
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Centralized log collection and correlation
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Real-time threat data and indicators of compromise
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Advanced endpoint monitoring and protection
- Security Orchestration and Automation (SOAR): Automated incident response workflows
- Vulnerability Management Tools: Proactive identification of security weaknesses
For Saudi organizations, ensuring technology selections align with local requirements and regional threat landscapes is essential. Alnafitha’s security solutions offer proven frameworks designed specifically for the Saudi market, with deep understanding of local compliance requirements and threat actors.
Step 4: Building SOC Processes and Playbooks
What is an example of a SOC? Consider a financial institution that implemented a SOC to protect customer transactions. Their SOC implementation included:
- Documented incident response procedures for common threat scenarios
- Automated alert correlation to reduce false positives by 70%
- Integration with fraud detection systems for detailed monitoring
- Regular tabletop exercises to test response capabilities
- Continuous improvement based on threat intelligence from MITRE ATT&CK framework
Creating full scale playbooks ensures consistent, efficient responses to security incidents and accelerates your SOC operations maturity.
Step 5: Staffing and Training
The human element is crucial in SOC implementation. What does SOC mean in jobs? SOC roles represent some of the most critical positions in modern cybersecurity:
- SOC Analyst: Monitors alerts and performs initial investigations
- Incident Responder: Handles confirmed security incidents
- Threat Hunter: Proactively searches for hidden threats
- SOC Manager: Oversees operations and strategic direction
Understanding SOC Reports and Deliverables
What are the three types of SOC reports? While this typically refers to Service Organization Control reports (SOC 1, SOC 2, SOC 3) for service providers, in the context of SOC implementation, organizations should focus on three key operational reports:
- Incident Reports: Detailed documentation of security events and response actions
- Metrics Dashboards: KPIs tracking detection rates, response times, and resolved incidents
- Executive Summaries: High-level security posture updates for business leadership
These reports provide visibility into your SOC operations effectiveness and ROI, essential for maintaining stakeholder confidence and demonstrating compliance.
SOC Implementation for Different Business Contexts
What Does SOC Stand For in the Military?
What does SOC stand for in the military? While military contexts use SOC for Special Operations Command, business SOC implementation draws valuable lessons from military security operations:
- Layered defense strategies: Multiple security controls working together
- Clear command structures: Defined roles and rapid escalation procedures
- Intelligence-driven operations: Proactive threat hunting based on intelligence
- Continuous readiness: 24/7 operations and regular drills
SOC Implementation Across Industries
What does SOC mean for work varies by sector:
- Financial Services: Focus on transaction monitoring and fraud detection aligned with SAMA cybersecurity framework
- Healthcare: Patient data protection and compliance with data privacy regulations
- Retail: POS security and customer data protection
- Government: Critical infrastructure protection and national security
- Energy: Industrial control system security and operational technology protection
Saudi organizations in regulated industries face additional SOC implementation requirements from sector-specific authorities, making partnered approaches particularly valuable.
Defining SOC Services and Deliverables
What is a SOC service? It’s the full security monitoring and response offering that your SOC provides to the organization. What does a SOC do? Core services include:
- 24/7 security monitoring across all IT assets
- Threat detection and analysis using advanced analytics
- Incident response following established procedures
- Vulnerability management and patch coordination
- Security reporting for compliance and management
- Threat intelligence integration and analysis
Understanding what does a SOC mean in practical terms helps set realistic expectations for SOC implementation outcomes and ensures alignment between security teams and business leadership.
Advanced SOC Concepts: Beyond Basic Implementation
What is a SOC and a Greaser?
While what is a SOC and a greaser refers to characters from “The Outsiders,” the metaphor applies to security: just as different groups had distinct roles, effective SOC implementation requires diverse skill sets working together—from technical analysts to business-focused security leaders.
SOC in Business Context
What is a SOC in business? It’s a strategic investment that:
- Reduces cybersecurity risk and potential losses
- Enables compliance with regulatory requirements
- Protects brand reputation and customer trust
- Supports digital transformation initiatives
- Provides competitive advantage through security excellence
For B2B organizations, SOC implementation demonstrates commitment to protecting partner and customer data—a critical differentiator in today’s market.
Incident Response: The Heart of SOC Operations
What are the 7 steps of incident response? Effective SOC implementation must incorporate a structured incident response process:
- Preparation: Developing plans, tools, and training
- Identification: Detecting and validating security incidents
- Containment: Limiting incident impact and spread
- Eradication: Removing threats from the environment
- Recovery: Restoring systems to normal operations
- Lessons Learned: Analyzing incidents to improve defenses
- Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed throughout
SOC Implementation Best Practices for Saudi Organizations
Based on successful SOC implementation projects across the Kingdom, consider these recommendations:
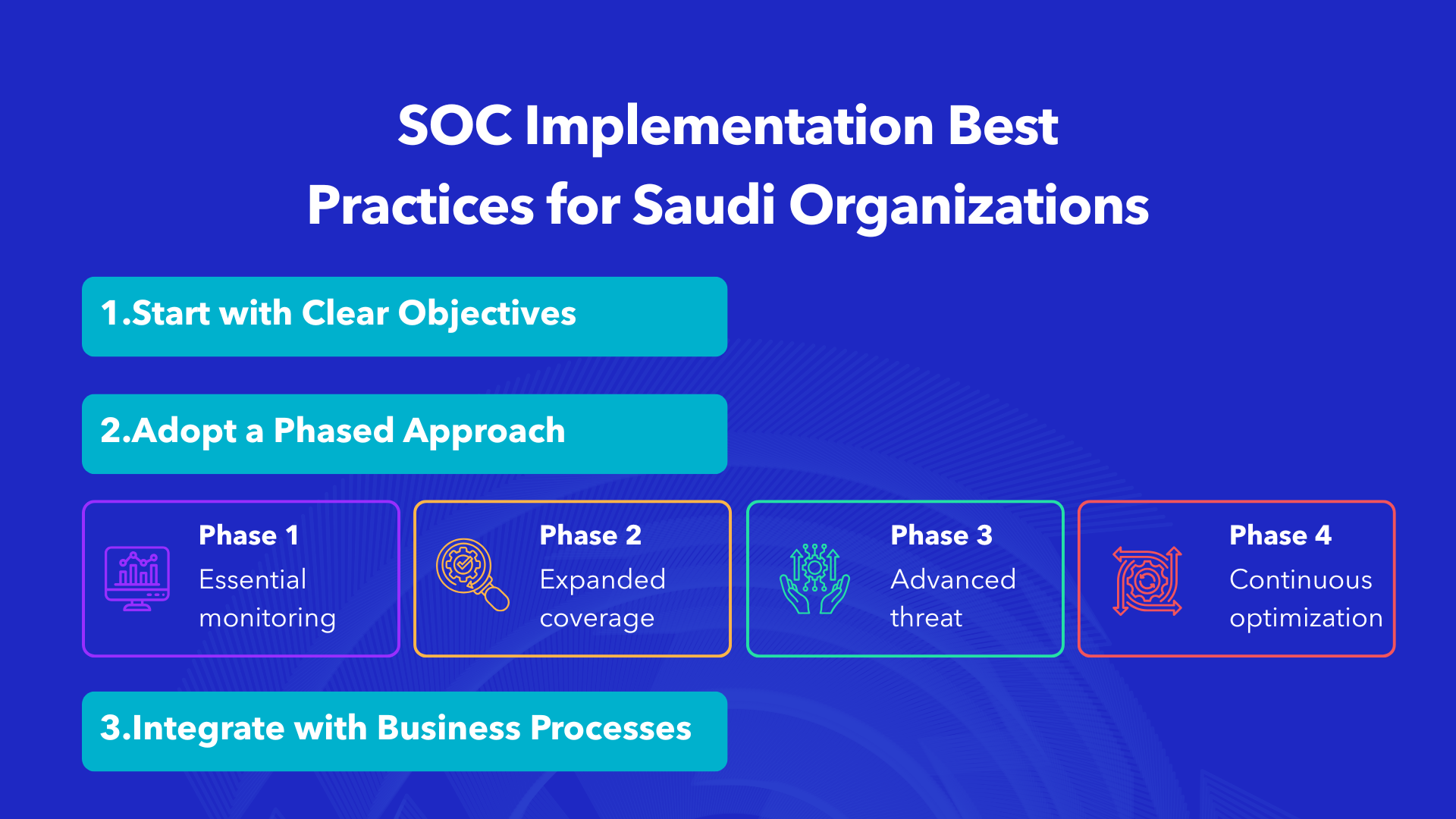
Start with Clear Objectives
Define what success looks like for your SOC implementation. Whether it’s achieving NCA compliance, reducing incident response times, or protecting specific critical assets, clear goals guide decision-making throughout the implementation journey.
Adopt a Phased Approach
Rather than attempting complete SOC implementation immediately, consider a phased rollout:
- Phase 1: Essential monitoring for critical assets
- Phase 2: Expanded coverage and improved detection capabilities
- Phase 3: Advanced threat hunting and automation
- Phase 4: Continuous optimization and maturity enhancement
Integrate with Business Processes
Successful SOC implementation doesn’t operate in isolation. Integrate security operations with:
- IT service management using ITIL frameworks
- Risk management frameworks
- Business continuity planning
- Vendor and third-party risk programs
Measure and Improve Continuously
Establish KPIs for your SOC operations:
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR)
- False positive rates
- Incident closure rates
- Coverage of critical assets
Regular assessments ensure your SOC implementation evolves with your threat landscape and maintains alignment with business objectives.
Addressing Common SOC Implementation Challenges
Saudi organizations frequently encounter these obstacles during SOC implementation:
Talent Shortage
The global cybersecurity skills gap affects Saudi Arabia significantly. Address this through:
- Partnership with managed security service providers
- Investment in training and development programs
- Collaboration with universities and training institutions like SANS Cyber Academy
- Attractive compensation packages for security professionals
Technology Complexity
Modern SOC implementation involves numerous integrated technologies. Simplify through:
- Careful vendor selection with integration capabilities
- Phased technology deployment
- Complete documentation and knowledge management
- Regular technology assessments and optimization
Budget Constraints
SOC implementation requires significant investment. Optimize costs by:
- Starting with essential capabilities and expanding gradually
- Leveraging cloud-based security platforms
- Considering managed SOC services for predictable costs
- Demonstrating ROI through risk reduction metrics
The Future of SOC Implementation in Saudi Arabia
As Saudi Arabia continues its digital transformation journey under Vision 2030, SOC implementation will evolve to address emerging challenges:
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhanced threat detection and automated response capabilities
- Cloud Security: Protecting hybrid and multi-cloud environments
- IoT Security: Monitoring industrial and consumer IoT devices
- 5G Networks: Securing next-generation connectivity infrastructure
- Quantum Computing: Preparing for post-quantum cryptography challenges
Organizations investing in SOC implementation today position themselves for tomorrow’s security challenges while building organizational resilience.
Taking the Next Step in Your SOC Implementation Journey
For Saudi business leaders and IT decision-makers, SOC implementation represents a critical investment in organizational resilience. Whether you’re exploring how to implement a SOC for the first time or enhancing existing security operations, success requires strategic planning, appropriate resources, and experienced guidance.
Understanding what SOC implementation is is just the beginning. The real value comes from executing a thoughtful, phased approach that aligns with your business objectives, compliance requirements, and risk profile.
Ready to explore SOC implementation for your organization? Consider these immediate next steps:
- Conduct a security maturity assessment to understand your current state
- Define your security objectives and success criteria
- Evaluate build vs. buy options for your specific needs
- Engage with experienced partners who understand the Saudi market
- Develop a phased roadmap with clear milestones and metrics
The journey to effective SOC operations begins with awareness and commitment from business leadership. By investing in proper SOC implementation, Saudi organizations not only protect their digital assets but also enable secure innovation and sustainable growth in an increasingly connected world.
Partner with Alnafitha for Your SOC Implementation Success
Don’t navigate the complexities of SOC implementation alone. Alnafitha brings deep expertise in cybersecurity solutions tailored specifically for Saudi organizations, with proven experience helping businesses across the Kingdom build robust security operations centers.
Our team understands the unique challenges facing Saudi businesses—from NCA compliance requirements to regional threat landscapes—and provides end-to-end support for your SOC implementation journey.
Ready to strengthen your organization’s security posture?
Contact our security experts today to discuss your SOC implementation requirements and discover how Alnafitha can help you build a world-class security operations capability that protects your business and enables growth.
