Navigating SAMA compliance requirements for access management can feel overwhelming for Saudi Arabian businesses. Whether you’re a financial institution, fintech startup, or payment service provider, understanding the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority’s cybersecurity framework is crucial for your organization’s success. This SAMA compliance guide will walk you through every step of implementing robust access management controls that meet regulatory standards.
What is SAMA Compliance and Why Access Management Matters
SAMA compliance refers to adherence to the cybersecurity regulations set forth by the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority. The SAMA compliance framework specifically requires financial institutions to implement stringent access management controls to protect sensitive data and financial systems.
Access management is at the heart of SAMA compliance because it controls who can access what resources within your organization. According to industry research, poor access controls are often the root cause of data breaches and regulatory violations that can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
Key SAMA Compliance Requirements for Access Management:
- Identity verification and authentication protocols
- Role-based access control (RBAC) implementation
- Privileged access management (PAM) systems
- Regular access reviews and certifications
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enforcement
- Session management and monitoring
Step 1: Conduct a Detailed SAMA Compliance Assessment
Before implementing any access management controls, you need to understand where your organization currently stands regarding SAMA compliance. This SAMA compliance checklist approach ensures you don’t miss critical requirements.
Initial Assessment Components:
Current Access Inventory Review:
- Document all user accounts across your systems
- Identify privileged accounts and service accounts
- Map access permissions to business roles
- Review existing authentication mechanisms
Gap Analysis Against SAMA Requirements: Create a detailed SAMA compliance checklist that includes:
- Authentication strength requirements
- Authorization granularity standards
- Audit trail completeness
- Data classification and access controls
- Incident response procedures
Risk Prioritization: Focus your SAMA compliance efforts on the highest-risk areas first. Typically, this includes:
- Administrative and privileged accounts
- Systems processing sensitive financial data
- External-facing applications and APIs
- Third-party integrations and vendor access
Consider partnering with professional IT assessment services to ensure complete coverage of all compliance requirements.
Step 2: Design Your SAMA Compliance Framework for Access Management
A well-designed SAMA compliance framework serves as the foundation for all your access management initiatives. This framework should align with both SAMA requirements and international best practices, including NIST, ISO 27001, and PCI-DSS standards.
Core Framework Components:
Identity Governance Structure:
- Establish clear ownership for identity management processes
- Define roles and responsibilities for access provisioning
- Create approval workflows for different access types
- Implement automated user lifecycle management
Access Control Policies: Your SAMA compliance policies should address:
- Minimum password requirements and complexity
- Multi-factor authentication mandates
- Session timeout and concurrent session limits
- Privileged access approval processes
- Emergency access procedures
Technical Architecture Requirements:
- Centralized identity and access management (IAM) platform
- Integration with existing business applications
- Real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities
- Automated provisioning and deprovisioning
- Complete audit logging
Leverage advanced IT management solutions to build a robust technical foundation for your compliance framework.
Step 3: Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication is a cornerstone requirement of SAMA compliance. The regulation mandates MFA for all privileged users and recommends it for all users accessing sensitive systems.
MFA Implementation Strategy:
Phase 1: Privileged Users
- Start with system administrators and database administrators
- Implement hardware tokens or smart cards for highest-privilege accounts
- Establish backup authentication methods
Phase 2: Standard Users
- Deploy mobile authenticator apps organization-wide
- Integrate MFA with single sign-on (SSO) solutions
- Provide user training and support documentation
Phase 3: External Access
- Extend MFA requirements to vendor and partner access
- Implement conditional access policies based on location and device
- Establish guest access procedures with appropriate restrictions
SAMA Compliance MFA Best Practices:
- Use FIDO2 or similar standards-based authentication
- Implement adaptive authentication based on risk context
- Maintain detailed logs of all authentication events
- Regularly review and update authentication policies
- Plan for MFA bypass procedures in emergency situations
Consider implementing effective cybersecurity solutions that include advanced authentication capabilities aligned with SAMA requirements.
Step 4: Establish Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Implementing proper role-based access control is essential for SAMA compliance. RBAC ensures users only have access to resources necessary for their job functions, following the principle of least privilege.
RBAC Implementation Process:
Role Definition and Mapping:
- Analyze job functions across your organization
- Create standardized role definitions
- Map roles to specific system permissions
- Document role inheritance and segregation requirements
Permission Modeling:
- Define granular permissions for each application and system
- Create permission bundles for common access patterns
- Establish approval matrices for sensitive permissions
- Document exception handling procedures
Role Assignment and Maintenance:
- Implement automated role assignment based on HR data
- Create workflows for role changes and promotions
- Establish regular role certification processes
- Monitor for role creep and unauthorized access accumulation
Common RBAC Challenges in SAMA Compliance:
- Over-privileged accounts: Regular access reviews help identify and remediate excessive permissions
- Orphaned accounts: Implement automated deprovisioning when employees leave
- Shared accounts: Eliminate shared accounts and implement proper individual accountability
- Emergency access: Establish proper break-glass procedures with full audit trails
Utilize automated IT management solutions to streamline RBAC implementation and maintenance processes.
Step 5: Implement Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged access management is a critical component of SAMA compliance, requiring special attention to accounts with elevated permissions. The SAMA compliance framework specifically addresses privileged account security with detailed requirements for monitoring and control.
PAM Implementation Components:
Privileged Account Discovery:
- Scan all systems to identify privileged accounts
- Classify accounts based on risk and access level
- Document account ownership and business justification
- Identify service accounts and system accounts
Password Management:
- Implement automated password rotation for privileged accounts
- Use password vaults to store and manage credentials securely
- Establish check-out/check-in procedures for shared accounts
- Monitor password usage and access patterns
Session Management:
- Record and monitor all privileged user sessions
- Implement real-time session monitoring and alerting
- Establish session timeout policies
- Create session analytics and reporting capabilities
Just-in-Time (JIT) Access:
- Implement temporary access elevation procedures
- Require business justification for privileged access requests
- Automate access revocation after specified time periods
- Maintain complete audit trails for all JIT access
Step 6: Establish Access Review and Certification Processes
Regular access reviews are mandatory under SAMA compliance regulations. These reviews ensure access permissions remain appropriate and aligned with business needs, as outlined in the framework’s governance requirements.
Access Review Framework:
Review Frequency and Scope:
- Quarterly reviews for privileged accounts
- Semi-annual reviews for standard user accounts
- Annual complete access certifications
- Event-driven reviews for role changes or incidents
Review Process Workflow:
- Automated Data Collection: Generate access reports from all systems
- Manager Review: Line managers certify appropriate access for their team members
- Risk-Based Analysis: Focus additional scrutiny on high-risk access patterns
- Remediation Tracking: Document and track all access changes
- Exception Handling: Establish procedures for disputed or unclear access
Review Documentation Requirements:
Your SAMA compliance documentation should include:
- Review schedules and participants
- Access certification sign-offs
- Remediation actions taken
- Exception approvals and business justifications
- Trend analysis and continuous improvement recommendations
SAMA Compliance Review Best Practices:
- Use automated tools to streamline the review process
- Implement risk-based sampling for large user populations
- Provide clear guidance and training to reviewers
- Establish escalation procedures for unresolved access issues
- Maintain historical records of all access decisions
Implement effective IT service management solutions to support efficient access review processes.
Step 7: Implement Continuous Monitoring and Alerting
SAMA compliance requires continuous monitoring of access-related activities. This proactive approach helps detect potential security incidents and ensures ongoing compliance.
Monitoring Strategy Components:
Real-Time Activity Monitoring:
- Monitor authentication attempts and failures
- Track privileged account usage patterns
- Detect unusual access patterns and anomalies
- Monitor system and application access logs
Behavioural Analytics:
- Establish baseline user behavior patterns
- Implement machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection
- Create risk scores for user activities
- Generate alerts for suspicious behavior patterns
Compliance Monitoring:
- Track compliance with access control policies
- Monitor policy exceptions and violations
- Generate compliance dashboards and reports
- Provide automated compliance attestation
Key Monitoring Metrics for SAMA Compliance:
- Authentication success/failure rates
- Privileged account usage frequency
- Access policy violations
- Account lockout incidents
- Failed access attempts by source
- Time-based access pattern anomalies
Consider implementing advanced monitoring and management solutions that provide complete visibility into your access management environment.
Step 8: Develop Incident Response Procedures
Your SAMA compliance program must include robust incident response procedures specifically for access-related security events. The framework requires detailed incident management capabilities.
Incident Response Framework:
Incident Classification:
- Define severity levels for access-related incidents
- Establish escalation criteria and notification procedures
- Create response timelines for different incident types
- Document communication protocols with SAMA
Response Procedures:
- Immediate containment actions (account lockouts, access revocation)
- Investigation and forensic analysis procedures
- Evidence collection and preservation protocols
- Recovery and remediation procedures
- Lessons learned and process improvement
Documentation Requirements: Your SAMA compliance incident documentation should include:
- Incident timeline and chronology
- Impact assessment and affected systems
- Response actions taken
- Root cause analysis
- Preventive measures implemented
Step 9: Establish Vendor and Third-Party Access Controls
Managing third-party access is a critical aspect of SAMA compliance, especially given the interconnected nature of modern financial services. The framework includes specific requirements for third-party cybersecurity management.
Third-Party Access Management:
Vendor Risk Assessment:
- Evaluate vendor security controls and compliance status
- Require compliance attestations and certifications
- Conduct security assessments of vendor environments
- Establish contractual security requirements
Access Provisioning Controls:
- Implement separate access control procedures for vendors
- Require individual accountability (no shared accounts)
- Establish time-limited access with automatic expiration
- Implement additional monitoring for third-party activities
Ongoing Management:
- Regular review and certification of vendor access
- Continuous monitoring of third-party activities
- Incident response coordination with vendors
- Contract renewal security requirement updates
Step 10: Create Your SAMA Compliance Documentation Package
Complete documentation is essential for demonstrating SAMA compliance to regulators and auditors.
Required Documentation Components:
Policy Documentation:
- Access control policies and procedures
- Identity governance framework documents
- Risk assessment methodologies
- Incident response procedures
Technical Documentation:
- System architecture diagrams
- Access control matrix and role definitions
- Integration specifications and data flows
- Security control implementation details
Operational Documentation:
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- User training materials and records
- Access review procedures and schedules
- Monitoring and alerting configurations
Compliance Evidence:
- Access review certifications and sign-offs
- Audit reports and findings
- Remediation tracking and status
- Continuous monitoring reports
SAMA Compliance Documentation Best Practices:
- Maintain version control for all policy documents
- Establish document review and approval workflows
- Create centralized document repositories with proper access controls
- Implement document retention and archival procedures
- Provide regular training on documentation requirements
Common SAMA Compliance Challenges and Solutions
Understanding common implementation challenges helps ensure your SAMA compliance program succeeds:
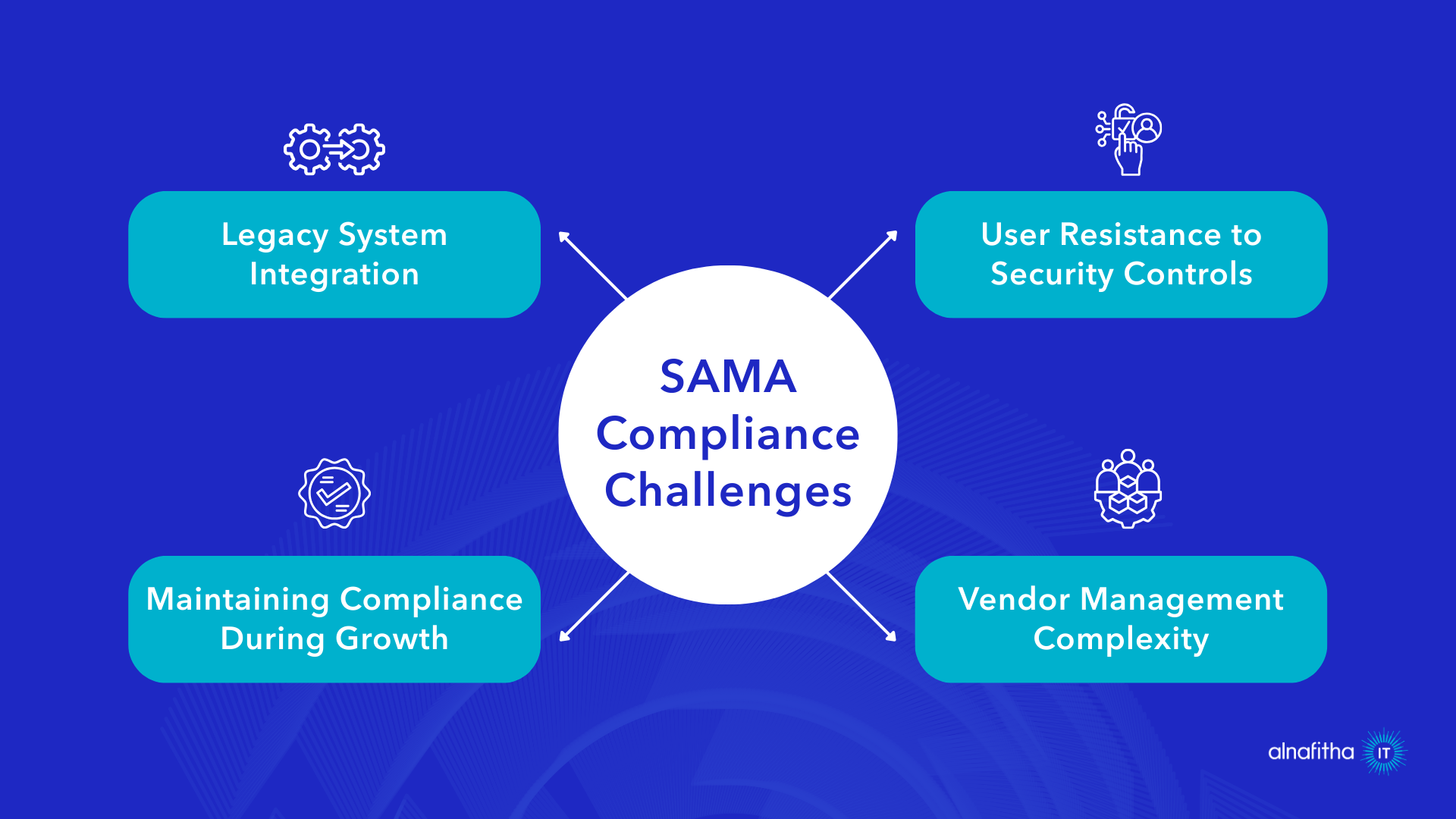
Challenge 1: Legacy System Integration
Problem: Legacy systems may not support modern authentication methods
Solution: Implement privileged access management solutions that can bridge legacy systems with modern IAM platforms..
Challenge 2: User Resistance to Security Controls
Problem: Users may resist MFA and other security measures
Solution: Implement user-friendly authentication methods and provide thorough training programs
Challenge 3: Maintaining Compliance During Growth
Problem: Rapid business growth can outpace security control implementation
Solution: Implement automated provisioning and scalable IAM platforms that grow with your business
Challenge 4: Vendor Management Complexity
Problem: Managing access for multiple vendors and partners
Solution: Implement centralized vendor access management with standardized procedures and automated monitoring. Explore detailed IT management solutions that support third-party access control.
Measuring SAMA Compliance Success
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your SAMA compliance program:
Compliance Metrics:
- Policy compliance rate (target: >95%)
- Access review completion rate (target: 100%)
- Privileged account coverage (target: 100%)
- MFA adoption rate (target: 100% for privileged users)
Security Metrics:
- Authentication failure rate trends
- Privileged account usage patterns
- Policy violation incidents
- Time to detect and respond to access anomalies
Operational Metrics:
- Access provisioning time
- User support ticket volume
- Automation rate for routine tasks
- Cost per user for access management
Technology Solutions for SAMA Compliance
Implementing the right technology stack is crucial for SAMA compliance success. Consider these key solution areas:
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Platforms
- Centralized user provisioning and deprovisioning
- Role-based access control enforcement
- Self-service password reset capabilities
- Automated compliance reporting
Privileged Access Management (PAM) Solutions
- Credential vaulting and rotation
- Session recording and monitoring
- Just-in-time access provisioning
- Risk-based access analytics
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Real-time monitoring and alerting
- Compliance reporting and dashboards
- Threat detection and response
- Audit trail management
For detailed technology implementation support, consider working with experienced cybersecurity solution providers who understand SAMA compliance requirements.
Next Steps for Your SAMA Compliance Journey
Implementing SAMA compliance for access management is an ongoing process that requires continuous attention and improvement. Here are your immediate next steps:
- Conduct a detailed gap assessment using the SAMA compliance checklist provided in this guide
- Prioritize implementation based on risk and regulatory requirements
- Engage stakeholders across IT, security, and business units
- Select appropriate technology solutions that support your SAMA compliance framework. Consider working with experienced IT service providers who understand local compliance requirements.
- Develop a phased implementation plan with clear milestones and success criteria
Remember that SAMA compliance is not a destination but a journey of continuous improvement. Regular assessment, monitoring, and updating of your access management controls will ensure ongoing compliance and security effectiveness.
By following this detailed SAMA compliance guide, your organization will be well-positioned to meet regulatory requirements while building a robust foundation for secure access management that supports business growth and innovation in the Saudi Arabian market.
Start Your SAMA Compliance Journey
Don’t navigate the complex world of SAMA compliance alone. Our team of certified cybersecurity experts specializes in helping Saudi Arabian businesses implement detailed access management solutions that meet all SAMA regulatory requirements.
Get started today with a free consultation:
- Complete SAMA compliance gap assessment
- Customized implementation roadmap
- Expert guidance from certified professionals
- End-to-end support throughout your compliance journey
